The most striking conclusions

This week the Dutch National Coordinator for Security and Counterterrorism published it’s yearly report ‘ Cybersecuritybeeld Nederland 2018’. The most important conclusion is anything but reassuring ‘The scale and seriousness of the digital threat in the Netherlands are still considerable and continue to evolve. There is a continuous digital threat to national security. The subtitel is less concealing ‘Attackers successful due to lack of basic measures’.
The Dutch society and economy have become completely dependent on digital resources. The consequences of attacks and dropouts can be large and even disruptive.How is possible that we take so few countermeasures against cybercrime? First an overview of the most important findings.
Sabotage and disruption by states greatest threat to national security
The report states on the basis of geopolitical motives, states are increasingly resorting to digital attacks on other countries, organizations or individuals. They aim to acquire strategic information through espionage, influencing public opinion or democratic processes and disruption or even sabotage of vital systems. Last week the FBI published a warning to reboot your router, related to a VPNFilter
malware which was also mentioned by Bruce Schneider in his blogpost. Altought it’s not proven the complexitity of the code involved indicates the involvement of state actors. These kind of advanced malware and persistent threats are a growing threat in the rat race between states and cyber criminals.Attackers remain successful due to lack of basic measures
Apart from very sophisticated attack methods most organizations are still successfully attacked with simple methods. Updates of the lastest code and software agains vulnerabilities are simply forgotten or not even on the agenda. Patching and system hardening is very important to do, but clearly stil not everyone is convinced about these basis principles of IT security.
Cyber attacks are very profitable and easy to implement and come with little risks for the attacker. Unsafe products eg. IoT devices and services are a fundamental cause of many incidents. The call for security standards and regulations for IoT devices is getting louder and louder.
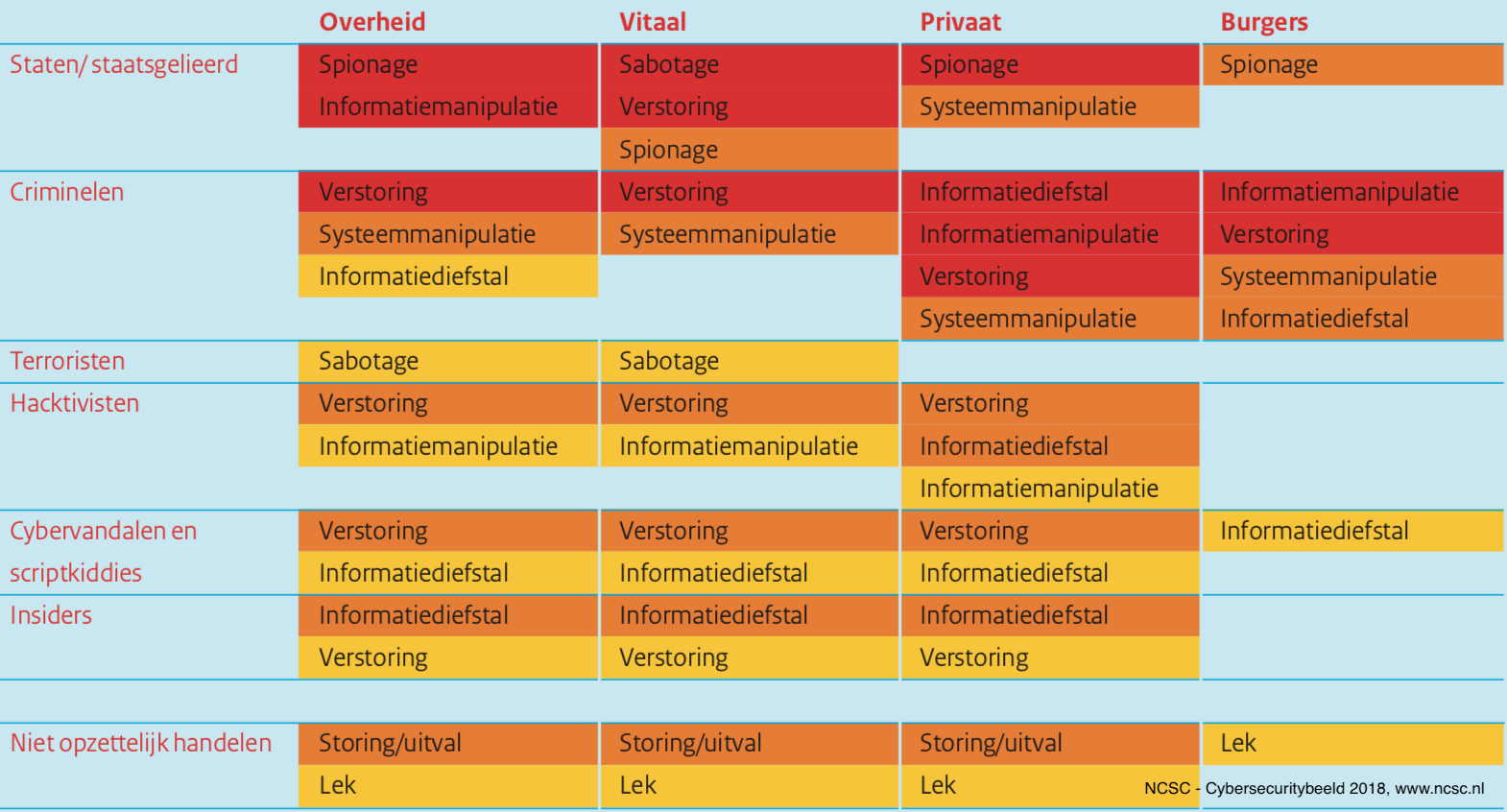
Main conclusions
- State actors are considered to cause the greatest threat. In the past year the world was startled by sophisticated attacks a WannaCry and Petya which caused a huge damage all around the world.
- Supplier chains increase vulnerability; a clear example was NotPetya that spread through an update of Ukrainian accounting software.
- A range of actors (state, criminal, hactivist) is extremely interested in stealing personal data. This is also noteworthy as since 25thof May the GDPR is now effective, which means that if a company has not taken adequate measures it could face a serious fine.
- The threat of terrorists and hacktivists seems stable
- Cybercrime as a service, attack facilitators, increase accessibility of attack methods. On the one hand, these are criminals who trade stolen information, such as credit card data or personal data, for financial gain. They sell information that can then be used for an attack. On the other hand, these are actors who realize facilities for attackers, for example by renting out botnets.
If you read the reports of the NCSC year on year, it shows to my opinion that the main threats remain stable although the upcoming state actors should be a main concern to us all. The attacks become more and more sophisticated which makes it more difficult to prevent. What makes that many are still ignorant about the threat of cybercrime. As members of a digital society we should all become more and more aware of the risk of cybercriminals and educate ourselves in this topic. This week the Dutch Government launched the Digital Trust Centerto support SME entrepreneurs. Entrepreneus can now call the DTC for practical information and advice on cybercrime related topics as they publish regularly practical tips as guidance. The community of information security professionals is growing and are quite cooperative and willing to help. If you feel uncomfortable do not hesitate and ask an expert for guidance!
You can download the full NCSC report here.